Is Now the Time to Rotate Into Ethereum?
The Case for ETH Now
Preface
In our previous article How Far Can The Bull Run, we explored Bitcoin’s price action and potential scenarios in the ongoing bull market. This time, we’ll turn our attention to Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
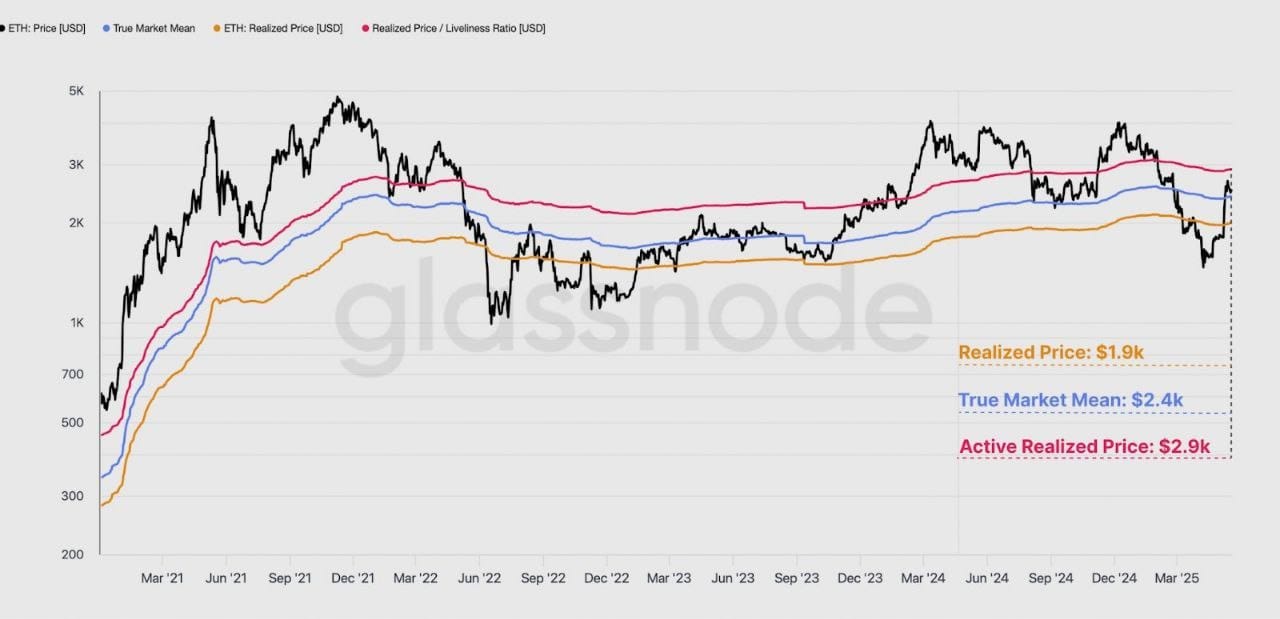
After dipping to a low of around $1,400 in early April, Ethereum has, much like Bitcoin, experienced a relief rally, climbing back to the $2,400-$2,500 range at the time of writing. This relief rally is very crucial, as Ethereum has managed to recover above key price levels, most notably, reclaiming its realized price at around $1,900 and reaching its true market mean.
A key factor behind the rally is the strong net inflow in Ethereum ETFs, with particularly notable +58,85K ETH recorded on April 25, 2025, when Ethereum was trading at $1,768. Such inflows suggest that institutional investors view Ethereum prices below $1,900 as undervalued, signaling strong institutional interest at these levels.
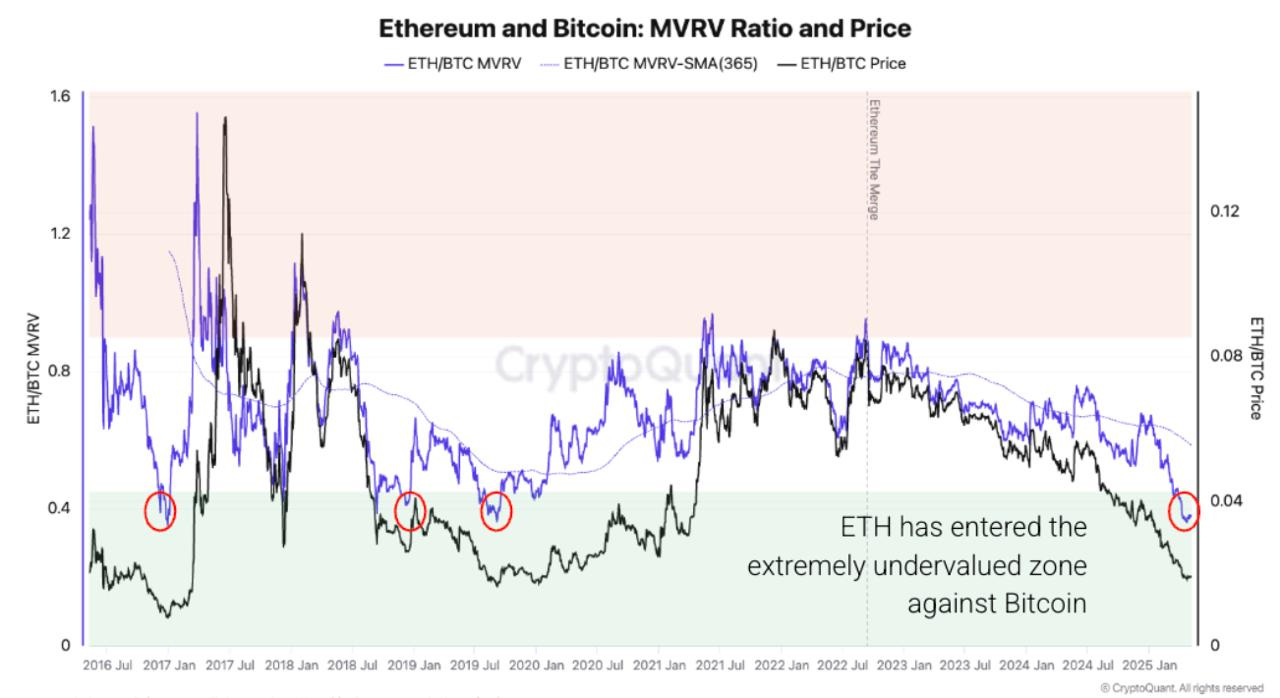
From a valuation perspective, Ethereum’s extreme undervaluation relative to Bitcoin —reflected in the ETH/BTC MVRV ratio—appears to present a compelling buying opportunity. Historically, low levels in this metric have often preceded periods of Ethereum outperforming Bitcoin. This forms the core question we’ll explore in this article: Is now the right time to rotate into Ethereum?
Where Ethereum Stands in the Current Market Landscape
Before diving deeper into the price action, it’s very important to understand the fundamental state of Ethereum as a network.
Ethereum Recent’s Pectra Upgrade Explained
Ethereum’s latest upgrade called Pectra officially went live in May 2025. Unlike previous upgrades that often introduced major changes, Pectra focuses on refining what’s already there, making Ethereum faster, more efficient, and cheaper to use. Let’s break down the changes introduced by Pectra in simple terms.
Blob Throughput Increase: Cheaper and Faster for Layer 2s
One of Pectra’s main improvements is the increase in blob capacity. Blobs, which introduced in 2024, are special data packages that allow Layer 2 blockchain like Arbitrum and Optimism to post data to Ethereum at a lower cost.
Previously, Ethereum support only 3 blobs per block, which sometimes wasn’t enough to meet growing demand. For example, on June 19, 2024, the average blob fee spiked to $42 —up from nearly zero the day before—because the limited supply of blobs couldn’t handle the demand.
With Pectra, the number of blobs per block has been doubled to 6, helping rollups handle data more efficiently while keeping fees low. This improvement is very essential for ensuring smoother Layer 2 experiences, cheaper transactions, more apps, and better scalability overall.
Staking Changes: Easier for Solo Stakers
Another key improvement in the Pectra upgrade is focusing on making staking more efficient, especially for solo stakers. Before Pectra, validators could only earn rewards on up to 32 ETH. If you want to stake more, you had to create multiple validators, which added complexity, costs, and technical challenges. With Pectra, this limit has been raised to 2,048 ETH per validator.
This means stakers now can now consolidate multiple validators into a single one, top up existing validators, and earn compounding rewards more efficiently. It simplifies the staking process and reduces the need for managing multiple validator accounts, making it much easier for solo stakers or those running their own setups at home.
Since the Pectra upgrade went live in May 2025, over 11,000 validators have successfully consolidated, representing around 359,000 ETH combined (as of late May). As a result, the overall number of active validators has decreased by over 16,000, reflecting a trend towards fewer but larger validators. This not only makes staking more capital efficient but also reduces the overall load on Ethereum’s network.
While the average amount of ETH staked per validator has only slightly increased from around 32 ETH to 32.4 ETH so far, this trend is expected to continue. As more stakers consolidate, we’ll likely see the distribution of validator sizes shift, with more validators holding larger balances.
Calldata Cost: Reducing Bloat on the Network
Another important change in the Pectra upgrade focuses on keeping Ethereum’s network fast and efficient by managing how much data is stored in each block. In Ethereum, “calldata” is a type of data that gets posted to the blockchain, kind of like extra notes attached to each transaction. If there’s too much calldata, it can make blocks too large and slow down the network.
To solve this, Pectra makes it more expensive to use calldata. To be more specific, the cost of calldata has been increased from 16 gas to 40 gas per byte. This encourages developers to use calldata more efficiently and reduce unnecessary bloat. At the same time, earlier in February 2025, Ethereum increased the overall gas limit (the maximum amount of data that can fit in a block) by 20%. So, while calldata is now more expensive, the network can still handle more transactions overall.
Ethereum Competitive Landscape
Ethereum’s recent Pectra upgrade are part of a long-term effort to enhance the network’s scalability while staying true to its core priorities of security. This balance is crucial because the way people think about Ethereum is fundamentally different from how people see Bitcoin. While Bitcoin is often viewed as a store of value, Ethereum is designed to be a network: a foundational layer for decentralized applications, and new forms of economic activity. This vision means that Ethereum must be able to scale effectively so developers and users can build on top of it without compromising the network’s security or decentralization.
However, this multi-facetet approach also introduces trade-offs. Ethereum’s focus on security can make it seem slower or less efficient compared to other chains that focus narrowly on scalability, such as Solana. It is well known for its low fees, which makes it more familiar and attractive for users making smaller of more frequent transactions.
Ethereum’s challenges are deeply tied to the blockchain trilemma—the idea that no blockchain can optimize for scalability, security, and decentralization all at once without compromise. Ethereum’s design prioritizes security and decentralization, making it more robust and reliable, but this also limits scalability compared to other blockchains that focus on high-speed, low-cost transactions like Solana. In crypto, you can’t have it all—there’s always a trade-off.
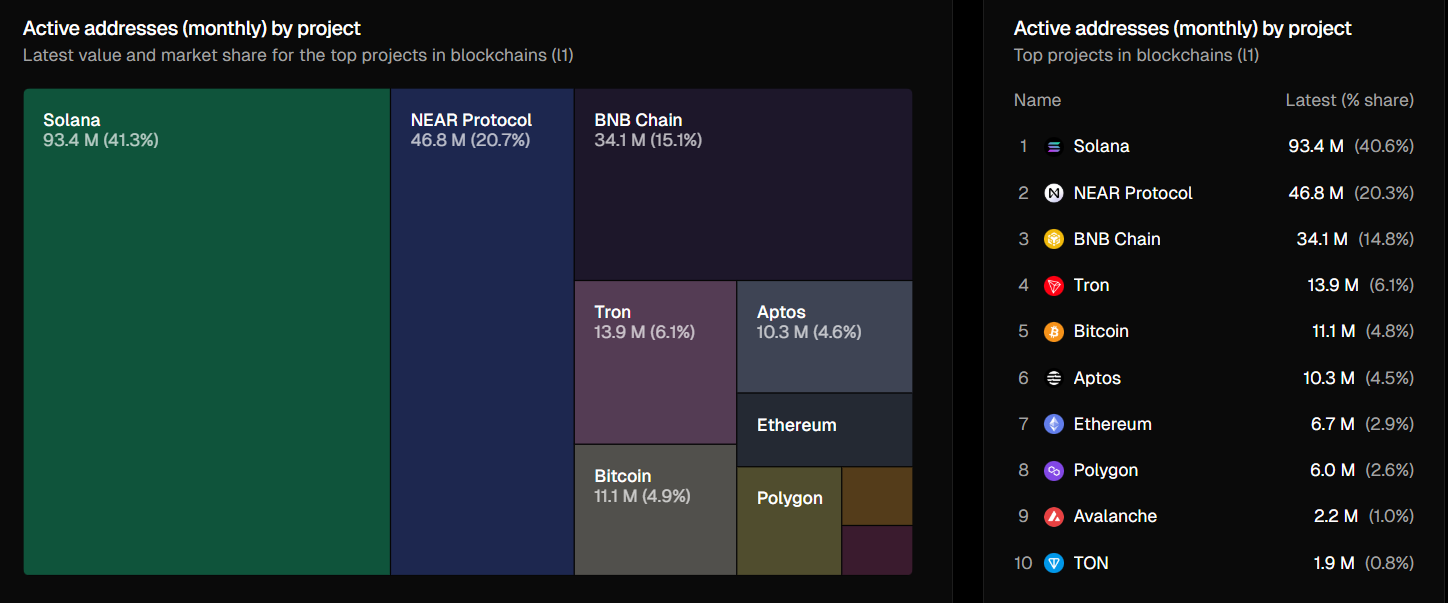
While Ethereum is widely recognized as the most secure and decentralized smart contract platform, it’s important to ask—is that what users truly prefer? Based on recent data, Ethereum holds just 2.9% of the market share for active addresses over the past 30 days, while chains with lower fees—Solana (40.6%), NEAR Protocol (20.3%), and BNB Chain (14.8%)—dominate.
This suggests that users tend to favor lower fees and favor lower fees and faster transactions over higher levels of security. Ultimately, while Ethereum’s security is a key differentiator, it comes with trade-offs that may limit user adoption in the short term—especially in areas where affordability and speed are top priorities. This difference in approach helps explain why Ethereum’s development roadmap often sparks debate. Currently, Ethereum competes across three key areas: data availability, execution (supporting complex smart contracts), and monetary properties. While no other blockchain matches Ethereum’s strength across all three fronts, competition is closing the gap.
Don’t get us wrong, Ethereum is still the king when it comes to Total Value Locked (TVL), which refers to the total assets deposited or staked in its ecosystem. As of now, Ethereum holds an impressive US$61.2 billion in TVL, far surpassing any other blockchain. This reflects the trust and confidence the market has in Ethereum as a secure and robust platform. However, the big question remains: can Ethereum scale quickly enough to maintain its leadership? If it takes too long, users and developers may migrate to other chains that offer faster and cheaper alternatives, which could eventually erode Ethereum’s position. But if Ethereum can deliver, it has the potential to remain the backbone of a secure, scalable, and decentralized digital economy for years to come.
Price Action and Key Concerns
Our current bullcycle has been particularly challenging for Ethereum. So far in this cycle, ETH has struggled to break past the $4,000 level, falling short of its previous all-time high of around $4,800. This inability to surpass its prior peak has raised questions about Ethereum’s momentum in this cycle, especially when compared to Bitcoin that have managed to set new highs.
This caution is also reflected in Ethereum’s Short-Term Bubble Risk indicator, which measures how “overheated” the market is by comparing the current closing price to its 20-week simple moving average (SMA). For Ethereum, the Short-Term Bubble Risk has not even reached overheat levels in this cycle, with a peak of only 57.25 so far. This is notably lower than past cycles, where the oscillator often crossed into higher risk zones, signaling potential local tops.
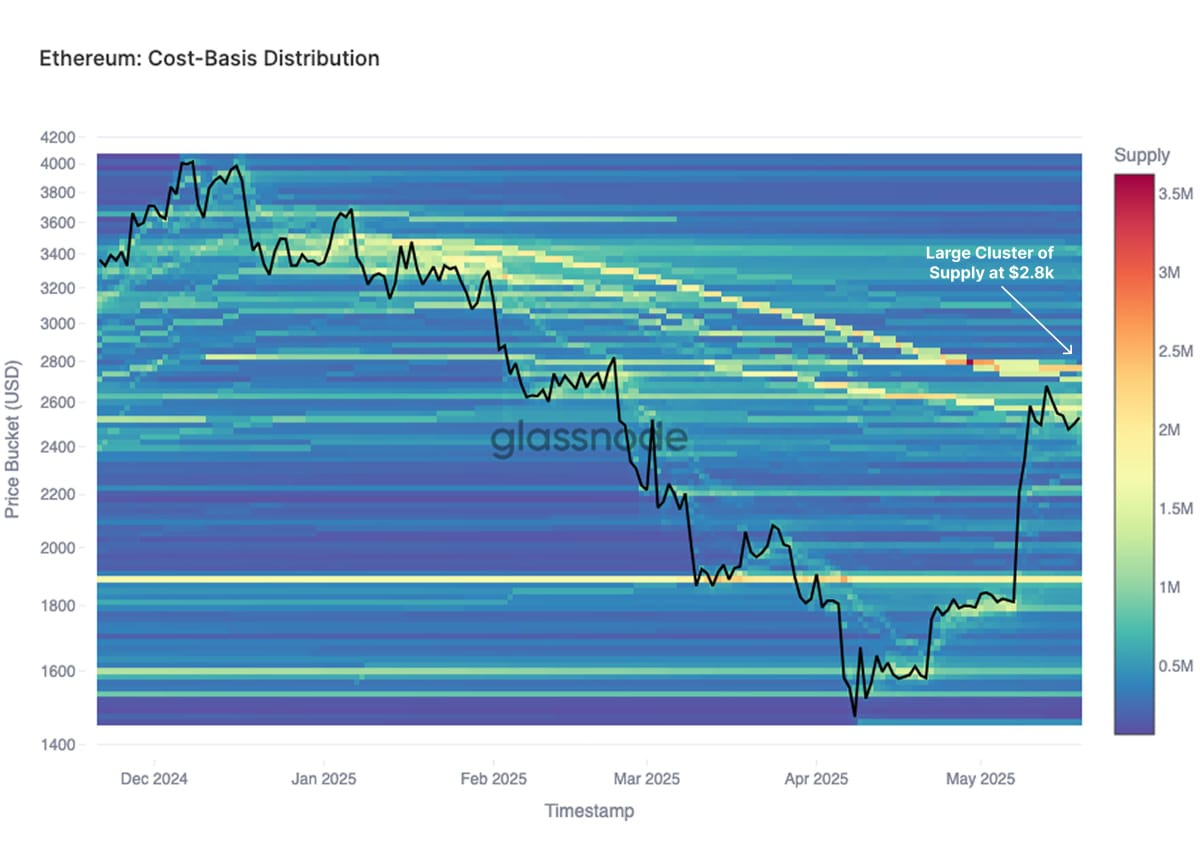
While we previously discussed how Ethereum’s decline below its realized price presents a buying opportunity, it’s also important to note that Ethereum’s rally appears to have paused at the $2,800 level. This pause can be attributed to a significant cluster of investor cost basis levels around $2,800. As Ethereum approaches this zone, many holders who were previously underwater may see an opportunity to de-risk and exit positions at or near breakeven, creating sell-side pressure that temporarily halts further upside momentum.
More on that, there are few major concerns that could prevent Ethereum from breaking out into a full-blown parabolic rally:
Ethereum Still Moves with Bitcoin
Let’s face the reality, Ethereum hasn’t decoupled from Bitcoin. If Bitcoin approaches its potential cycle top and starts correcting, Ethereum will likely follow. As long as this correlation holds, Ethereum’s upside is limited by Bitcoin’s market cycle.
Low Burn Rate and Rising Supply
Post-Dencun, the burn rate has dropped to its lowest point since The Merge. Coupled with a high issuance rate, Ethereum is facing real inflationary pressures. Supply keeps growing, but demand hasn’t matched it—putting a lid on price momentum.
Losing Ground in Revenue and Store of Value (SoV)
Ethereum is fighting on two fronts, and losing on both:
Ultrasound Money (Revenue Side)
Ethereum’s main revenue from Layer 1 is declining because the most profitable parts—like MEV (extra value from transaction ordering) and congestion fees—have shifted mostly to Layer 2 solutions. These L2s now capture over 90% of the profits, while Ethereum is left with less valuable tasks like settlement and data availability.
On top of that, some apps are grabbing their own MEV revenue (for example, Aave with Chainlink SVR) and even launching their own app-specific chains (like Uniswap). As Ethereum keeps expanding space for L2s, transaction fees are competing to be as low as possible, which makes it harder for Ethereum to maintain strong revenue unless on-chain activity grows massively. And even if activity increases, it’s unclear how much of that revenue ETH itself will actually get compared to the L2s and apps.
Programmable Money (Store of Value Side)
ETH as a “gas token” is becoming less visible because of technologies like account abstraction and paymasters. Users don’t need to hold ETH to pay gas fees—they can use other tokens or stablecoins instead. On L2s, ETH has to compete with every other asset for attention, and its SoV narrative is diluted because ETH bridged to L2s carries the same risks as any other bridged asset. Adding to this, stablecoins dominate crypto’s product-market fit. Most users prefer trading in USD terms rather than holding volatile assets like ETH.
Final Thoughts
We continue to see Ethereum as the most reliable and resilient Layer 1 network in the space, supported by a strong foundation and an active developer community. While Bitcoin remains the primary beneficiary of limited market liquidity, Ethereum still has a chance to outperform in the short term—especially during periods of favorable narratives or strong inflows into ETH-based instruments.
However, several concerns remain. Given the current macroeconomic landscape and restrictive monetary policy, it may be difficult for Ethereum to sustain a full parabolic rally in this cycle. Structural headwinds, including capital concentration in Bitcoin and liquidity constraints, continue to limit the upside potential. Even so, Ethereum remains worth monitoring closely. It offers swing trade opportunities—particularly when accumulating near the realized price and taking profits around key cost-basis levels where supply clusters are dense.












👍👍
hail queen eth